חדשות המחקר
Avraham Jacobson, Sivan Spitzer, Yanay Gorelik, Michael Edelstein: Barriers and enablers to vaccination in the ultra-orthodox Jewish population: a systematic review (Front Public Health . )
The Jewish Ultra-Orthodox (UO) population is an under-vaccinated minority group that has been disproportionally affected by outbreaks of vaccine-preventable diseases (VPD) such as measles and polio. Underlying reasons remain poorly characterized. We aimed to identify vaccination barriers and enablers in this population.
Adi Francis: Weaker SARS-CoV-2 vaccine responses in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease with advanced liver fibrosis (Vaccine X . )
SARS-CoV-2 vaccine responses that could harbor potential risks to chronic liver diseased patients. Aims: To assess immune response following Pfizer's SARS-CoV-2 vaccine in patients with different liver fibrosis severities of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD).

Tzipora Falik-Zaccai: Clinical and molecular features in a cohort of Middle Eastern patients with epidermolysis bullosa (Pediatr Dermatol .)
Epidermolysis bullosa (EB) features skin and mucosal fragility due to pathogenic variants in genes encoding components of the cutaneous basement membrane. Based on the level of separation within the dermal-epidermal junction, EB is sub-classified into four major types including EB simplex (EBS), junctional EB (JEB), dystrophic EB (DEB), and Kindler EB (KEB) with 16 EB-associated genes reported to date. We ascertained a cohort of 151 EB patients of various Middle Eastern ethnic backgrounds.

Humanitarian Outpatient Pediatric Endeavor (HOPE): A Novel Specialist Ambulatory Health-Care Concept in Conflict Areas (Disaster Med Public Health Prep .)
With the collapse of the medical system in Syria, Israel began providing Syrians with humanitarian aid, first to the war-injured and then general medical treatment. We developed a novel specialist ambulatory care concept to provide medical care for Syrian children.
(Matti Mizrachi, Einat Levy, Amiel A Dror, Eyal Sela, Sergey Kutikov, Masad Barhoum, Ohad Ronen, Maayan Gruber)
Gassan Moady, BateL Yelin, Rania Sweid, Shaul Atar: C-Reactive Protein Can Predict Outcomes in Patients With Takotsubo Syndrome (Int J Heart Fail .)
Takotsubo syndrome (TTS) is a form of reversible cardiomyopathy often preceded by mental or physical stressors and predominantly affects elderly women. Several cardiac and inflammatory biomarkers are involved in the pathogenesis of the disease. We aimed to investigate the correlation of C-reactive protein (CRP) level with left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) and clinical outcomes in patients with TTS.
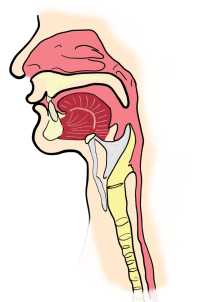
Ohad Ronen: Treatment of recurrent acute tonsillitis-a systematic review and clinical practice recommendations (Front Surg . )
There is an ongoing debate on the indications for tonsil surgery in both children and adults with recurrent acute tonsillitis. The aim is to provide practical recommendations for diagnostics and treatment for recurrent acute tonsillitis including evidence-based decision making for tonsillectomy.

Enav Yefet: The efficiency of cabergoline versus pyridoxine for lactation inhibition - a randomized controlled trial (Am J Obstet Gynecol . )
Some mothers may seek lactation inhibition on personal, social, or medical grounds. The common drug used for lactation inhibition is cabergoline. Several adverse effects and contraindications are known for this drug. Its use is contraindicated for patients with hypertensive disorders and fibrotic, cardiac, or hepatic diseases. Pyridoxine (Vitamin B6) has also been used for this indication, with no significant adverse effects, following studies that demonstrated its efficacy.

Shai Stern: Interpretation of Heart and Lungs Sounds Acquired via Remote, Digital Auscultation Reached Fair-to-Substantial Levels of Consensus among Specialist Physicians (Diagnostics (Basel) . )
Technological advancement may bridge gaps between long-practiced medical competencies and modern technologies. Such a domain is the application of digital stethoscopes used for physical examination in telemedicine. This study aimed to validate the level of consensus among physicians regarding the interpretation of remote, digital auscultation of heart and lung sounds.
Edo Y Birati: Left Ventricular Unloading With Impella Versus IABP in Patients With VA-ECMO: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis (Am J Cardiol . )
Venoarterial extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (VA-ECMO) use for circulatory support in cardiogenic shock results in increased left ventricular (LV) afterload. The use of concomitant Impella or intra-aortic balloon pump (IABP) have been proposed as adjunct devices for LV unloading. The authors sought to compare head-to-head efficacy and safety outcomes between the 2 LV unloading strategies.
Ohad Ronen: A Meta-analysis of Surgical Outcomes of T4a and Infranotch T4b Oral Cancers (Oncol Ther .)
Objective: To determine the overall surgical outcomes of infranotch T4b oral cancers and compare them with T4a oral cancers.
Nasser Sakran: Bariatric and Metabolic Surgery in Patients with Situs Inversus: a Systematic Review (Obes Surg . )
Laparoscopic surgery in patients with obesity with situs inversus (SI) may pose interesting challenges to diagnosing and managing due to the mirror image anatomy. Since in SI patient's organs are displaced, the surgery requires high levels of precision and hand-eye coordination. SI and bariatric surgery may pose challenges for the surgical team.
Nour Ibrahim: Chronic Rhinosinusitis After Maxillary Advancement Orthognathic Surgery (Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol .)
Maxillomandibular advancement (MMA) remains an effective procedure for the management of obstructive sleep apnea (OSA). Maxillary advancement may lead to anatomical changes that impair paranasal sinus drainage, leading to chronic sinus inflammation. The aim of this study was to describe the clinical features and outcomes of patients suffering from chronic rhinosinusitis (CRS) following MMA.

Oren Ziv , Elad Rubin, Omry Koren: Successful weight regain attenuation by autologous fecal microbiota transplantation is associated with non-core gut microbiota changes during weight loss; randomized controlled trial (Gut Microbes .)
We previously reported that autologous-fecal-microbiota-transplantation (aFMT), following 6 m of lifestyle intervention, attenuated subsequent weight regain and insulin rebound for participants consuming a high-polyphenol green-Mediterranean diet. Here, we explored whether specific changes in the core (abundant) vs. non-core (low-abundance) gut microbiome taxa fractions during the weight-loss phase (0-6 m) were differentially associated with weight maintenance following aFMT.

Shirin Hamed Azzam, Amir Nama, Haneen Jabaly Habib: The Effect of Ptosis Surgery on Meibomian Glands and Dry Eye Syndrome (Ophthalmic Plast Reconstr Surg . )
Investigates the effect of ptosis surgery on dry eye disease as measured by dry eye parameters and meibomian gland function.